

Luckily, creating a Blob from a plain-text value is as simple as calling the Blob constructor and passing in the text value:ĭownloading Text Using Blobs, URL.createObjectURL(), And The Anchor Download Attribute In JavaScript Of course, in order to use the URL.createObjectURL() method, we need to have a Blob. But, if you're generating a lot of these URLs, you can control the memory consumption more granularly by removing old Blob URIs with the URL.revokeObjectURL(blogURI) method. Depending on what your application is doing, this may or may not be a concern. When you create a Blob URI, the browser holds onto the referenced memory until the document is unloaded or, until you explicitly revoke the URL. This method takes a Blob (or Blob-like object) and returns a String that can be used in any place that a URL might be used (such as an HREF attribute). This reference will be generated by the URL.createObjectURL() method. Except, instead of a Data URI, we're going to point the "href" attribute to an in-memory object reference.
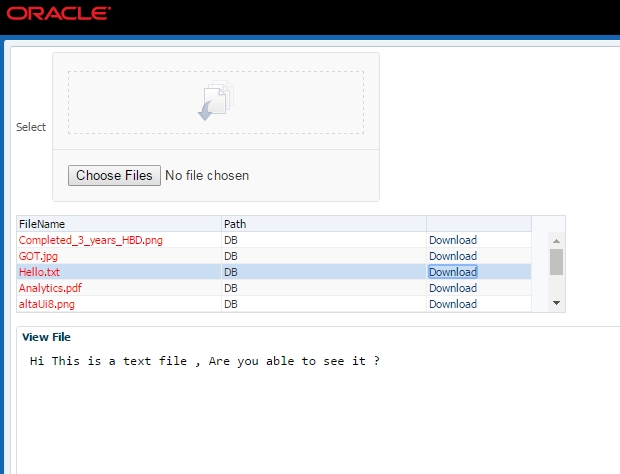
In this demo, we're going to be using a similar approach. Href="**data:**text/plain charset=utf-8." In the previous demo, I was setting an anchor tag's "href" attribute to point to a Data URI in the form of: View this code in my JavaScript Demos project on GitHub. Run this demo in my JavaScript Demos project on GitHub.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
